# MyBatis源码-缓存
MyBatis 缓存使用及如何实现
# 缓存的作用
MyBatis 支持1级、2级缓存,减少了数据库查询的频次,提升了查询的效率。我们需要了解下 MyBatis 缓存的使用方式及源码逻辑,从而减少在使用缓存过程中出现的不必要的问题出现。
# 缓存效果
# 1级缓存
@Test
public void testLocalCache() throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession(true); // 自动提交事务
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
System.out.println(studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
System.out.println(studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
System.out.println(studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
sqlSession.close();
}
输出结果
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT id,name,age FROM student WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
TRACE [main] - <== Columns: id, name, age
TRACE [main] - <== Row: 1, 点点, 16
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
entity.StudentEntity@f79a760
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
entity.StudentEntity@f79a760
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
entity.StudentEntity@f79a760
从上面的测试当中可以看出,我们连续执行了3次查询操作,真正走到数据库进行查询的也就1次,后边的2次查询走了缓存,并且从输出的对象内存地址发现是一个对象。
如果我们对数据进行增、删、改操作,然后再次查询是否还会走缓存呢?
@Test
public void testLocalCacheClear() throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession(true); // 自动提交事务
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
System.out.println(studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
System.out.println("增加了" + studentMapper.addStudent(buildStudent()) + "个学生");
System.out.println(studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
sqlSession.close();
}
输出结果
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT id,name,age FROM student WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
TRACE [main] - <== Columns: id, name, age
TRACE [main] - <== Row: 1, 点点, 16
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
entity.StudentEntity@1eb6749b
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: INSERT INTO student(name,age) VALUES(?, ?)
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 明明(String), 20(Integer)
DEBUG [main] - <== Updates: 1
增加了1个学生
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT id,name,age FROM student WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
TRACE [main] - <== Columns: id, name, age
TRACE [main] - <== Row: 1, 点点, 16
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
entity.StudentEntity@24d4d7c9
从上面执行结果可以看出,当对数据进行变更操作时,缓存就会失效。
那如果 SqlSession 不一致时,是否会走缓存呢?
@Test
public void testLocalCacheScope() throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession1 = factory.openSession(true); // 自动提交事务
SqlSession sqlSession2 = factory.openSession(true); // 自动提交事务
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession1.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
StudentMapper studentMapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
System.out.println("studentMapper读取数据: " + studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
System.out.println("studentMapper读取数据: " + studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
System.out.println("studentMapper2更新了" + studentMapper2.updateStudentName("小岑",1) + "个学生的数据");
System.out.println("studentMapper读取数据: " + studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
System.out.println("studentMapper2读取数据: " + studentMapper2.getStudentById(1));
}
输出结果
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT id,name,age FROM student WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
TRACE [main] - <== Columns: id, name, age
TRACE [main] - <== Row: 1, 点点, 16
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
studentMapper读取数据: entity.StudentEntity@3b220bcb
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
studentMapper读取数据: entity.StudentEntity@3b220bcb
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: UPDATE student SET name = ? WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 小岑(String), 1(Integer)
DEBUG [main] - <== Updates: 1
studentMapper2更新了1个学生的数据
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
studentMapper读取数据: entity.StudentEntity@3b220bcb
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT id,name,age FROM student WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
TRACE [main] - <== Columns: id, name, age
TRACE [main] - <== Row: 1, 小岑, 16
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
studentMapper2读取数据: entity.StudentEntity@618c5d94
当SqlSession 不一致时,在1级缓存下会出现读取脏数据的问题。
上面创建了两个 SqlSession ,studentMapper 连续查询了2次,第一次查询数据库,第二次是从缓存中取的,这个时候 studentMapper2 对数据进行变更,studentMapper 再次查询的时候还是走了缓存。
# 小结
1级缓存(默认1级缓存时开启的)只对单个 SqlSession 生效,当对数据进行变更操作时缓存会失效。
# 1级缓存相关源码
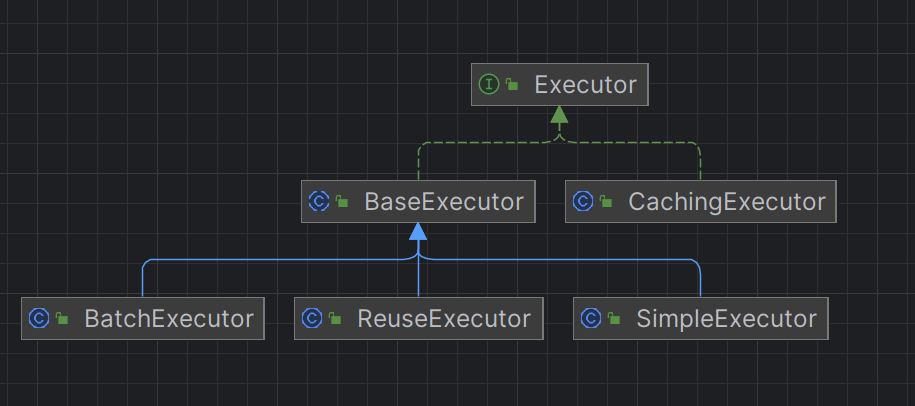
Executor : 是执行器接口,对数据库的所有操作都是通过这个入口进行的。
BaseExecutor :抽象类实现了执行器 Executor 接口,具体执行动作委托子类进行如 doUpdate、doQuery 。
BatchExecutor :批量操作,会缓存 Statement 对象,执行 update 的时候进行批量处理。
ReuseExecutor :重复执行器,会缓存 Statement 对象,其定义了一个Map<String, Statement>,将执行的sql作为key,将执行的Statement作为value保存。
当把 cacheEnabled 设置为 false 可以关闭2级缓存的情况下,这个时候会走 BaseExecutor类。
//BaseExecutor类
//查询相关的操作最终都会走到这里
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
//查询的sql语句及相关参数
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
//创建一个缓存key
//组装完成的缓存key 如:-1824555229:1330539143:mapper.StudentMapper.getStudentById:0:2147483647:SELECT id,name,age FROM student WHERE id = ?:1:development
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
//BaseExecutor类
//这个方法主要就是创建缓存的key,然后根据key查询缓存
//key主要有这几部分组成:Statement Id + Offset + Limmit + Sql + Params
@Override
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey();
//Statement Id
cacheKey.update(ms.getId());
//Offset 分页
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset());
//Limmit 分页
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit());
//Sql
cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql());
//处理参数 Params
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = ms.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry();
// mimic DefaultParameterHandler logic
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : parameterMappings) {
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
cacheKey.update(value);
}
}
if (configuration.getEnvironment() != null) {
// issue #176
cacheKey.update(configuration.getEnvironment().getId());
}
return cacheKey;
}
//BaseExecutor类
//执行查询方法 如果缓存有就从缓存中取,下面源码主要关注清除缓存的时机
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
//如果设置 flushCache="true" 每次查询都会清除之前的缓存
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
//先从缓存中取 如果没有从数据库中查询
//PerpetualCache localCache 内部是通过一个简单的hashmap 实现了缓存
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
//如果 设置localCacheScope = STATEMENT ,每次都会把缓存清除,也就是彻底关闭了1级缓存
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
# 2级缓存
2级缓存是 namespace 层面的,也就是 mapper 对应的相关 sql 。
配置开启方式如下:
<!--在 mybatis 配置文件里边配置开启 2级 缓存-->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<!--在 mapper 里边配置 cache 节点-->
<mapper namespace="mapper.StudentMapper">
<cache/>
</mapper>
@Test
public void testCacheWithUpdate() throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession1 = factory.openSession(true); // 自动提交事务
SqlSession sqlSession2 = factory.openSession(true); // 自动提交事务
SqlSession sqlSession3 = factory.openSession(true); // 自动提交事务
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession1.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
StudentMapper studentMapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
StudentMapper studentMapper3 = sqlSession3.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
System.out.println("studentMapper读取数据: " + studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
sqlSession1.close();
System.out.println("studentMapper2读取数据: " + studentMapper2.getStudentById(1));
studentMapper3.updateStudentName("方方",1);
sqlSession3.commit();
System.out.println("studentMapper2读取数据: " + studentMapper2.getStudentById(1));
}
输出结果
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT id,name,age FROM student WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
TRACE [main] - <== Columns: id, name, age
TRACE [main] - <== Row: 1, 方方, 16
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
studentMapper读取数据: entity.StudentEntity@619bfe29
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.5
studentMapper2读取数据: entity.StudentEntity@56ace400
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: UPDATE student SET name = ? WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 方方(String), 1(Integer)
DEBUG [main] - <== Updates: 1
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.3333333333333333
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT id,name,age FROM student WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
TRACE [main] - <== Columns: id, name, age
TRACE [main] - <== Row: 1, 方方, 16
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
studentMapper2读取数据: entity.StudentEntity@3234f74e
上面的实验是开启了2级缓存,创建了3个 SqlSession sqlSession1 查询后关闭,不影响 sqlSession2查询, sqlSession2 并且走了缓存。 sqlSession3 对数据进行更新操作, sqlSession2 查询的时候也重新从数据库查询,缓存失效。
# 小结
2级缓存是对整个 mapper 生效,多个 SqlSession 操作同一个 mapper 会走缓存并且也会影响缓存。
# 2级缓存源码
2级缓存创建基本和1级缓存一样,不同点在于获取缓存。
//Configuration类
//这个方法主要是创建一个执行器
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
//根据执行的类型创建不同的执行器
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
//重点看这里!!!
//如果开启2级缓存 就使用CachingExecutor对执行器进行一次装饰,得到一个 CachingExecutor 对象
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
//CachingExecutor类
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
//判断是否需要清除缓存
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, parameterObject, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//从TransactionalCacheManager缓存管理器中根据key查询是否有缓存信息
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
参考文章
- https://www.cnblogs.com/redwinter/p/16608113.html
- https://tech.meituan.com/2018/01/19/mybatis-cache.html (实验demo基本都是参考这个)
- https://www.cnblogs.com/wwct/p/12994222.html